Navigating the world of student loans can feel like wandering through a dense forest—each path lined with enticing opportunities but fraught with potential pitfalls. As the cost of education continues to rise, many students find themselves at a crossroads: to take the federal loan route, known for its protective measures and support, or to venture into the realm of private loans, which promise larger sums but frequently enough come with unexpected consequences. In this article, we will explore the fundamental differences between private and federal student loans, weighing their respective advantages and disadvantages. By shedding light on these two financial avenues,we aim to equip students and families with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions for their educational journeys. Whether you are looking to finance your college dreams or helping someone you care about, understanding the nuances of each option is essential in crafting a successful strategy for managing educational expenses.

Understanding the Basics of Student Loans and Their Types
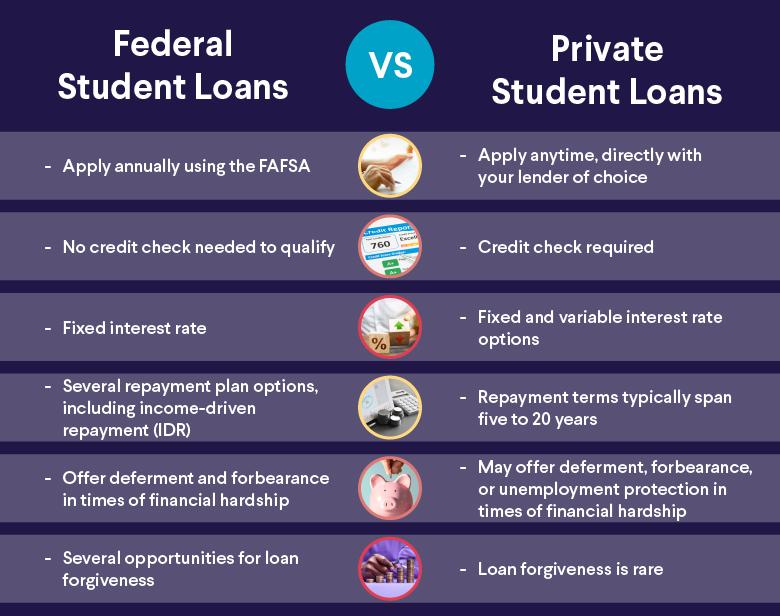
When navigating the world of student financing, understanding the types of loans available is essential. Federal student loans, offered by the government, provide students with various advantages. They typically feature lower interest rates and more flexible repayment options. Benefits can include income-driven repayment plans and deferment options,along with eligibility for loan forgiveness programs for those who work in public service roles.Moreover, these loans do not require a credit check, making them more accessible for many students.
On the other hand, private student loans are offered by banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions. While they can cover gaps in funding after federal loans and may offer larger sums for education costs, they come with their own set of pros and cons. Private loans tend to have higher interest rates, and the terms can vary considerably from lender to lender. Additionally,they frequently enough require a credit check,which can limit options for students with little or no credit history. Here’s a fast comparison of key aspects:
| Aspect | Federal Loans | Private Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Fixed, usually lower | Variable or fixed, often higher |
| Repayment Options | Flexible (e.g., income-driven) | Varies by lender |
| Credit Check | No | yes, often required |
| Loan forgiveness | Available | No |
Evaluating the Interest Rates: Private vs. federal Loans

Assessing Flexibility and Repayment Options in Student Financing
When weighing your options for financing education, it’s essential to carefully assess the flexibility and repayment strategies offered by both private and federal student loans. Federal student loans typically come with more lenient repayment terms, including options like Income-Driven Repayment Plans that adjust monthly payments based on your earnings. Additionally, federal loans offer forbearance and deferment options, providing temporary relief during hardship or while pursuing additional education. Some federal loans may even be eligible for loan forgiveness after qualifying payments over a specified period, making them an attractive option for many students.
On the contrary,private student loans frequently present fewer options for repayment flexibility.While these loans can cover educational costs that federal loans may not, they are usually less forgiving in terms of repayment plans. Most private lenders offer traditional repayment plans and may allow for deferment or forbearance only under strict circumstances.Here’s how the two compare:
| Aspect | Federal Loans | Private Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Repayment Flexibility | High; Income-Driven Plans & Forgiveness | Limited; Mostly Fixed Plans |
| Deferment Options | Available in Hardship | Limited availability |
| Loan forgiveness | Possible after 10-20 years | Not Typically Available |
while federal loans often come with the benefits of flexibility and multiple repayment options, private loans may suit students needing higher loan amounts but often lack those same supportive features. Considering your financial situation and potential job market is vital for making a decision that aligns with your long-term financial health.

Exploring borrower Protections and Benefits of Federal loans
When it comes to financing higher education, federal student loans offer a plethora of protections and benefits designed to support borrowers throughout their repayment journey. One of the most important advantages is income-driven repayment plans. these plans can help borrowers align their monthly payments with their income,making it easier to manage fiscal obligation without the risk of default. Additionally,federal loans often feature loan forgiveness programs like Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF),providing an avenue for those in qualifying careers to have their remaining debt discharged after a certain number of payments.
Furthermore, federal loans come with deferment and forbearance options, which allow borrowers to temporarily pause their payments during difficult financial times without adversely affecting their credit score. This is especially beneficial for recent graduates facing job market uncertainties. Moreover, federal loans offer fixed interest rates, providing predictability in repayment costs compared to the fluctuating rates often seen with private loans.the array of benefits tied to federal education financing makes it a compelling choice for many students.

Navigating the Application Process for Private and Federal Loans
Navigating the application process for student loans can be a daunting task, but understanding the differences between private and federal loans can lead to informed decisions. When applying for federal loans, the process typically begins with completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). This form collects financial and personal data to determine eligibility for various types of financial aid, including grants and federal student loans. Keep in mind that federal loans often offer repayment plans, such as income-driven repayment and loan forgiveness options, which can provide significant benefits to borrowers in certain situations. To enhance your chances of receiving the maximum aid, ensure all information is accurate and submitted on time.
On the other hand, the application process for private loans involves a different approach. Lenders typically require applicants to fill out an application that includes a credit check, income verification, and other eligibility requirements. Borrowers should carefully review terms and conditions, as interest rates, repayment options, and eligibility criteria can vary widely between lenders. Before proceeding with private financing, consider the following:
- Credit Score Impact: Private loans frequently enough depend on your credit score; a higher score can lead to better terms.
- Cosigner Options: If your credit score is low, consider enlisting a cosigner to improve your chances of approval.
- Loan Structure: Understand the interest rates and whether they are fixed or variable, as this affects your long-term costs.

Making an Informed Decision: Which Loan Is Right for You?
When considering your options for financing your education, it’s essential to weigh the pros and cons of both private and federal student loans. Federal student loans typically offer benefits that private loans may not. For instance,federal loans come with lower fixed interest rates,income-driven repayment plans,and potential forgiveness programs. They also provide essential protections,such as deferment and forbearance options,which can be invaluable during financial hardship. Though, the borrowing limits may not cover the entire cost of education, leading many students to explore private loans as a supplementary option.
On the flip side, private student loans can provide higher borrowing limits and are often unsecured, meaning they don’t require a cosigner if you have a good credit history. However, borrowers should be wary of the variable interest rates that can increase over time, and also the lack of flexible repayment options compared to federal loans. The following table summarizes key distinctions between private and federal loans:
| Feature | Federal Loans | Private Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Interest Rates | Fixed, generally lower | Variable or fixed, can be higher |
| Repayment flexibility | Income-driven options and forgiveness | Limited options |
| Credit Requirements | No credit check for most | Strong credit history needed |
| Loan Limits | Set limits based on degree level | Higher limits, can cover entire costs |
Insights and Conclusions
In the intricate landscape of student financing, choosing between private and federal student loans is akin to navigating a winding path filled with both opportunities and potential pitfalls. As we’ve explored the pros and cons of each option, it becomes clear that the decision is not one-size-fits-all. Federal loans offer a safety net of benefits, such as flexible repayment options and potential forgiveness programs—ideal for those prioritizing security in uncertain times. On the other hand, private loans may provide the allure of lower interest rates and higher borrowing limits, appealing to those who can confidently manage their financial futures.
Ultimately, your choice should hinge on personal circumstances, financial goals, and the unique tapestry of your academic journey. We encourage you to weigh your options carefully, seek advice, and explore all available resources, ensuring that whichever path you choose, it aligns with your aspirations and leads you toward a brighter, debt-managed future. As you stand on the threshold of this important decision, remember: knowledge is your best ally in transforming educational dreams into reality.

