Loan-to-Value ratio: Why It Matters for Secured Loans
When it comes to securing loans, understanding the Loan-to-Value (LTV) ratio is crucial. This financial metric can considerably influence your borrowing capacity, loan terms, and overall financial strategy. In this article, we will explore what the LTV ratio is, why it matters, and how you can leverage it to make informed decisions about your secured loans.
What is the loan-to-Value Ratio?
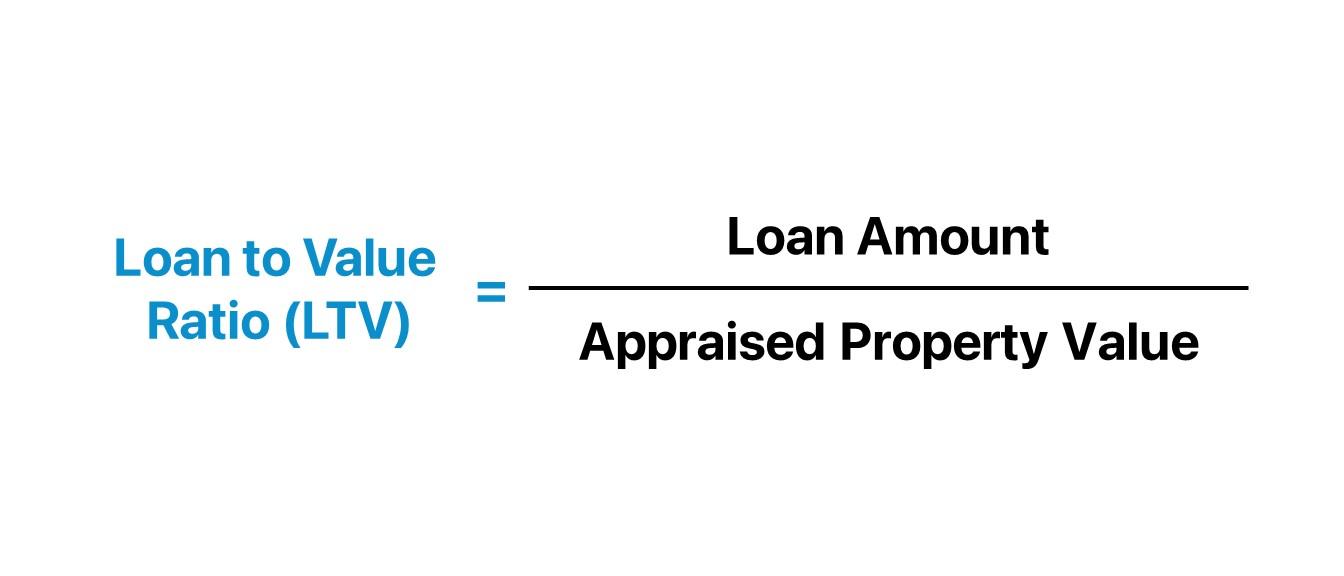
The Loan-to-value Ratio is a financial term that measures the ratio of a loan to the value of the asset being purchased. It is commonly used in real estate transactions and other forms of secured lending. The formula for calculating LTV is straightforward:
LTV = (Loan Amount / Appraised Value of the Property) x 100
For example, if you are buying a home valued at $300,000 and you take out a mortgage for $240,000, your LTV ratio would be:
LTV = ($240,000 / $300,000) x 100 = 80%
Why Does the Loan-to-Value Ratio Matter?
the LTV ratio is significant for several reasons:
- Risk Assessment: Lenders use LTV to gauge risk. The higher the LTV ratio, the riskier the loan is for the lender.
- Interest Rates: A lower LTV can frequently enough translate to lower interest rates, making loans more affordable over time.
- Mortgage Insurance: If your LTV ratio exceeds a certain percentage (typically 80% for conventional loans), you may be required to purchase private mortgage insurance (PMI).
- Loan Approval: Certain loan programs may have maximum LTV limits that borrowers must adhere to for approval.
Benefits of a Favorable Loan-to-Value Ratio
improving your LTV ratio offers numerous advantages:
- Lower Monthly Payments: A lower loan amount relative to the property value can reduce your monthly mortgage payments.
- Better Loan Terms: lenders are more likely to offer favorable terms, such as lower interest rates, to borrowers with lower LTV ratios.
- Increased Borrowing Power: A favorable LTV ratio can enhance your ability to secure additional financing, whether for home equity loans or other purposes.
Practical Tips for Managing Your Loan-to-Value Ratio
Here are some actionable steps you can take to improve your LTV ratio:
- Make a Larger Down Payment: The more you can put down upfront, the lower your LTV will be.
- Increase Property value: Upgrading your property can help increase its value, thus improving your LTV.
- Pay Down Your Loan: Regularly paying down your mortgage principal will lower your loan amount, positively impacting your LTV.
- Shop Around for Lenders: Different lenders may have varying policies regarding acceptable LTV ratios.
Case Studies: The Impact of LTV on Secured Loans
| Scenario | Loan Amount | Property Value | LTV Ratio | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 | $200,000 | $250,000 | 80% | Loan Approved; PMI Required |
| Case 2 | $250,000 | $300,000 | 83.3% | Loan Denied; High risk |
| Case 3 | $180,000 | $250,000 | 72% | Loan Approved; Low Interest |
First-Hand Experience: Navigating the LTV Ratio
When I decided to purchase my first home, I was initially unaware of the impact the LTV ratio would have on my mortgage options. After discussing my financial situation with a mortgage adviser, I learned that maintaining an LTV ratio below 80% would save me from needing PMI, which would save me hundreds of dollars each month. To accomplish this,I increased my down payment by saving diligently for a year. The result? A favorable interest rate and substantial long-term savings. This experience opened my eyes to the importance of the LTV ratio.
Conclusion
Understanding the loan-to-Value ratio is crucial for anyone considering a secured loan or mortgage. it serves as a vital indicator of risk for lenders and can significantly affect your borrowing capacity and interest rates. By managing your LTV ratio through larger down payments, home improvements, and consistent loan payments, you can not only enhance your borrowing power but also save money in the long run.Educate yourself about the LTV ratio, and make it an essential part of your financial planning strategy.